Understanding VAT: A Comprehensive Guide for UK Businesses
Value Added Tax (VAT) is a crucial aspect of running a business in the UK, and whether you’re just starting your business or have been operating for years, understanding VAT is essential for compliance, financial planning, and operational efficiency. For many businesses, VAT can seem like a complex and daunting subject, but with the right knowledge and guidance, it’s entirely manageable.
In this comprehensive guide, we will break down VAT registration, VAT rates, exemptions, reliefs, and the filing process to ensure your business complies with UK tax regulations and optimizes its financial standing. From small startups to established enterprises, this article will help you understand how VAT impacts your pricing, cash flow, and overall business strategy.
What is VAT?
VAT, or Value Added Tax, is a consumption tax applied to most goods and services in the UK. It is an indirect tax, meaning businesses collect VAT on behalf of the government. VAT is added to the sale price of most goods and services and must be passed on to the end consumer. The standard VAT rate is 20%, but there are exceptions, with reduced rates of 5% and 0% for specific goods and services.
How VAT Works:
When your business sells goods or services, you charge VAT on top of the sale price (this is known as output tax). When your business buys goods or services, you pay VAT to your suppliers (this is known as input tax). The difference between the VAT you’ve charged on sales and the VAT you’ve paid on purchases is either paid to HMRC or reclaimed.
Why is VAT Important for Businesses?

As a business owner, understanding VAT is vital for several reasons:
- Compliance with HMRC: Failing to adhere to VAT laws can lead to severe penalties and interest charges.
- Financial Planning: VAT affects your pricing strategy, cash flow, and overall profitability.
- Reclaiming VAT: Being VAT-registered allows you to reclaim VAT on business-related expenses, reducing your operational costs.
- Professional Image: VAT registration can lend credibility to your business, showcasing that you are an established and compliant entity.
VAT Registration: When Do You Need It?
Knowing when and how to register for VAT is one of the most crucial aspects of running a compliant business in the UK.
Mandatory VAT Registration
Businesses must register for VAT if their taxable turnover exceeds £85,000 over the past 12 months. Once your turnover surpasses this threshold, you must register with HMRC within 30 days. This ensures that you can legally charge VAT on your products and services.
Voluntary VAT Registration
Even if your business turnover is below the £85,000 threshold, you can still choose to voluntarily register for VAT. Voluntary registration offers several benefits:
- Reclaim VAT on Purchases: Businesses can reclaim VAT on purchases and expenses.
- Professional Credibility: Appearing as a VAT-registered entity can increase trust among clients and suppliers.
- Readiness for Growth: Registering early prepares your business for future expansion as your turnover exceeds the threshold.
How to Register for VAT
Here’s a step-by-step process for registering your business for VAT:
- Check If You Need to Register: Use HMRC’s online tool to check your turnover and determine if VAT registration is necessary.
- Gather Necessary Information: Have details such as your business’s contact info, turnover, and company registration number.
- Create a Government Gateway Account: If you don’t already have one, create an account with HMRC to access their online services.
- Complete the VAT1 Form: This form can be completed online on the HMRC website.
- Receive Your VAT Registration Certificate: HMRC will send you a VAT number and provide further instructions on submitting returns and payments.
VAT Rates and Categories: What You Need to Know
There are several VAT rates in the UK, each applicable to different categories of goods and services.
Standard Rate (20%)
The standard VAT rate applies to most goods and services in the UK. For example, consumer products like electronics, clothing, and household goods fall under the 20% VAT rate.
Reduced Rate (5%)
Certain goods and services, deemed essential or beneficial for policy reasons, are subject to the reduced VAT rate of 5%. Examples include:
- Energy-saving materials like insulation
- Children’s car seats
- Mobility aids for the elderly
Zero Rate (0%)
Some goods and services are subject to the zero VAT rate. While you don’t charge VAT on these goods or services, you can still reclaim VAT on the purchases related to these items. Examples include:
- Food (excluding hot takeaways and meals at restaurants)
- Children’s clothing
- Books, newspapers, and magazines
Exempt Goods and Services
Some goods and services are exempt from VAT entirely. This means businesses that deal in exempt goods cannot charge VAT, nor can they reclaim VAT on their related expenses. Examples of exempt goods include:
- Education and training services
- Healthcare services
- Financial services
VAT Returns: How and When to File
Filing VAT returns is a regular responsibility for VAT-registered businesses. A VAT return reports the VAT you’ve charged on sales and the VAT you’ve paid on purchases.
When to File VAT Returns
Most businesses must file VAT returns every quarter. However, businesses can opt for annual VAT returns if they are eligible.
How to File VAT Returns
- Calculate Your VAT: Subtract the VAT you paid on purchases (input tax) from the VAT you’ve collected on sales (output tax).
- Submit Online: Use HMRC’s online services or VAT-compliant software like QuickBooks or Xero to file your VAT return.
- Payment Deadline: Payments are typically due one month and seven days after the end of your VAT period.
VAT Accounting Schemes
HMRC offers several VAT accounting schemes to help businesses manage their VAT obligations more efficiently.
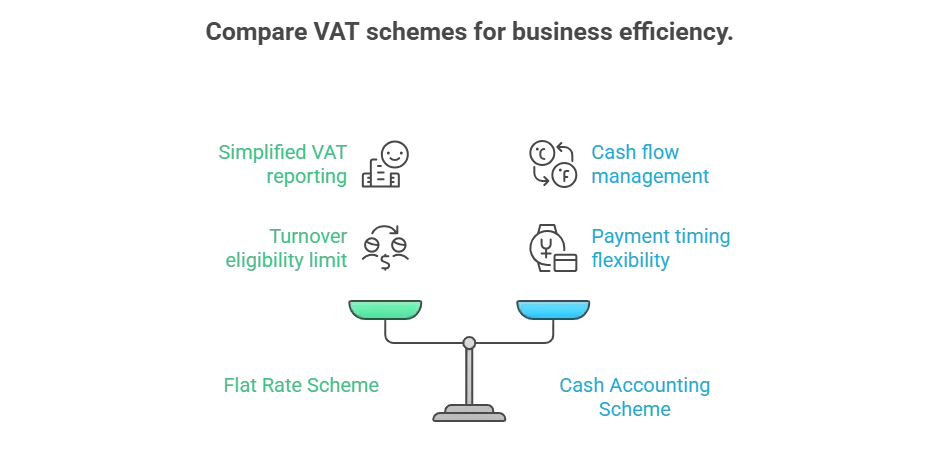
Flat Rate Scheme
The flat rate scheme simplifies VAT reporting by allowing businesses to pay a fixed percentage of their total turnover as VAT. This is available for businesses with a turnover under £150,000 and is ideal for businesses with minimal VAT expenses.
Cash Accounting Scheme
Under this scheme, businesses only pay VAT on sales when they receive payment and reclaim VAT on purchases when they pay their suppliers. This scheme helps with cash flow, particularly for businesses that experience delays in receiving payments.
Annual Accounting Scheme
This scheme allows businesses to file just one VAT return per year and make quarterly or monthly advance payments based on estimated VAT liabilities.
Common VAT Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Managing VAT can be tricky, and businesses often make mistakes that lead to penalties or missed opportunities. Here are some common VAT pitfalls and how to avoid them:
Undercharging VAT
Ensure that you are applying the correct VAT rates for your products or services. Regularly review your VAT rates to ensure accuracy.
Late VAT Payments and Returns
To avoid penalties, use accounting software to track VAT deadlines and set up reminders for filing VAT returns.
Not Reclaiming VAT on Purchases
Make sure to claim VAT on all eligible business expenses. Keep detailed records and receipts to support your claims.
Incorrect VAT Returns
Mistakes in your VAT return can lead to audits and fines. Ensure all calculations are accurate and consult a VAT expert if needed.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Conclusion: Stay Compliant and Optimize Your VAT Strategy
Understanding VAT is a fundamental aspect of managing a business in the UK. Whether you’re registering for VAT, navigating different VAT rates, or filing your returns, staying compliant with VAT regulations is key to maintaining financial health and avoiding penalties.
For businesses looking to optimize their VAT strategy, working with a professional accountant or VAT consultant can help ensure you’re claiming all eligible VAT, avoiding common mistakes, and making the most of available reliefs.Want to ensure your VAT compliance and optimize your returns? Contact us today for expert VAT guidance and start managing your VAT obligations with confidence.






